Mastering Auto Body Repair: From Damage Assessment to Quality Restoration
Collision and frame damage assessment is a critical first step in the auto body repair process, usin…….
In the vast and ever-evolving automotive industry, auto body repair stands as a critical process that ensures vehicles not only run but also look their best. The auto body repair process involves meticulous techniques to restore damaged or dented vehicle exteriors to their original condition, playing a pivotal role in safety, aesthetics, and customer satisfaction. This article aims to delve into the intricate world of auto body repair, offering readers a comprehensive guide to its ins and outs. We will explore its historical roots, global impact, economic significance, technological advancements, regulatory framework, challenges, and future prospects, providing valuable insights for industry professionals, enthusiasts, and anyone curious about this vital sector.
Auto body repair, also known as automotive bodywork or panel beating, is a specialized craft that focuses on restoring damaged vehicle bodies to their pre-accident condition. It involves the skilled manipulation of metal panels, frames, and structural components to fix dents, crashes, or other types of exterior damage. The process encompasses several key stages:
Inspection and Assessment: Technicians meticulously examine the damaged area, identifying the extent of the harm using specialized tools and software for precise measurements.
Dismantling: Depending on the repair, certain parts may need to be removed or temporarily dismantled to gain access to hidden damage or to facilitate easier repairs.
Reparation and Replacement: This is where the magic happens. Skilled technicians use a variety of tools, including hammers, dollies, and specialized equipment, to bend, straighten, and repair damaged panels. For severe cases, replacement parts may be required, ensuring original equipment manufacturer (OEM) quality.
Painting and Finishing: Once the metalwork is complete, the repaired area undergoes a meticulous painting process to match the vehicle’s original color precisely. This step ensures both aesthetic appeal and long-term corrosion protection.
Final Inspection and Quality Control: Before reinstallation, each repair is carefully inspected against strict quality standards to ensure perfect alignment, paint clarity, and structural integrity.
The roots of auto body repair can be traced back to the early days of automobiles when vehicles were primarily hand-crafted. In the 19th century, as cars became more mass-produced, the need for specialized repairs grew, leading to the emergence of dedicated body shops. The industry evolved significantly over time:
Early 20th Century: The advent of assembly line manufacturing in the automotive sector influenced body repair techniques, emphasizing efficiency and standardization.
Post-World War II Era: With the rise in personal vehicle ownership, auto body repair shops became common fixtures in communities, catering to a wide range of makes and models.
1980s – 1990s: The industry witnessed technological advancements, including computer-aided design (CAD) software for precise measurements and specialized tools for more efficient repairs.
21st Century: Modern auto body repair has embraced digital transformation with advanced CAD/CAM systems, robotic welding, and high-tech painting equipment, elevating the quality and speed of repairs.
Auto body repair is a global industry with significant economic and environmental implications. The scale and diversity of this sector vary across regions, influenced by factors such as vehicle ownership rates, road conditions, and local regulations.
North America: The United States and Canada have well-established auto body repair industries, driven by a high density of vehicles per capita. Advanced technologies and a mature insurance sector contribute to efficient repairs.
Europe: European countries exhibit diverse trends, with Germany and the UK renowned for their precision workmanship and advanced training programs. The continent’s stringent environmental regulations impact painting and finishing processes.
Asia Pacific: Rapidly growing economies like China and India are witnessing a surge in vehicle ownership, fueling the demand for auto body repair services. Japan has long been recognized for its high-quality repairs and innovative techniques.
Emerging Markets: In Latin America, Africa, and parts of Asia, the industry is expanding but faces challenges related to limited access to technology, skilled labor, and infrastructure.
Digitalization: The adoption of digital technologies, including CAD/CAM systems, virtual reality (VR) training, and online appointment booking, is gaining traction worldwide, enhancing efficiency and customer experience.
Sustainability: Environmental concerns are driving the industry towards eco-friendly practices, such as using water-based paints, optimizing energy consumption in repair shops, and promoting recycled materials.
Autonomous Vehicles: The rise of self-driving cars will impact body repair by potentially reducing accident-related damage, although new types of repairs related to sensor integration may arise.
Telematics and Insurance: Telematics devices and connected car technologies are transforming insurance processes, enabling faster claim settlements and more precise repair estimates.
The auto body repair industry plays a vital role in the global economy, with significant market dynamics and investment patterns shaping its landscape.
Global Market Value: According to a 2021 report by Grand View Research, the global automotive bodyshop market size was valued at USD 367.4 billion in 2020 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.8% from 2021 to 2028.
Regional Market Analysis: North America dominates the market, followed by Europe and Asia Pacific. The latter regions are projected to witness substantial growth due to increasing vehicle sales.
Franchise Businesses: Many auto body repair shops operate as franchises, offering standardized services under a well-established brand. This model attracts investors seeking a proven business concept.
Specialized Repair Centers: Some businesses specialize in specific areas like collision repair, paintless dent repair (PDR), or glass replacement, catering to niche markets and attracting targeted investments.
Technology Upgrades: Investing in advanced equipment, such as robotic welding systems and computer-aided design software, can enhance efficiency, reduce labor costs, and improve customer satisfaction.
Job Creation: The industry employs a significant number of skilled technicians, painters, and support staff, contributing to local economies.
Supply Chain Support: Auto body repair shops rely on a robust network of suppliers for parts, paints, and equipment, fostering interdependencies within the automotive ecosystem.
Insurance Sector: Body repair facilities have strong ties to insurance companies, participating in direct repair networks (DRNs) to facilitate claim settlements and streamline repairs.
Technology has revolutionized the auto body repair process, improving efficiency, accuracy, and customer satisfaction. Here are some significant advancements:
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) Software: CAD systems enable technicians to take precise measurements, design custom repair solutions, and simulate paint finishes before actual work begins. This technology ensures accurate repairs and minimizes errors.
Robotic Welding: Robotic arms have been introduced for tasks like spot welding, offering enhanced precision, speed, and consistency compared to manual methods.
Paintless Dent Repair (PDR): PDR techniques use specialized tools to gently push out dents from the vehicle’s outer panel, avoiding paint damage and reducing repair time significantly.
Online Booking and Communication: Many repair shops now offer online booking platforms and communication tools, allowing customers to schedule appointments, receive real-time updates, and access digital invoices.
Advanced Painting Technologies: Modern painting equipment employs state-of-the-art spray guns, automated lines, and advanced paint formulas to ensure fast drying times, superior color accuracy, and durable finishes.
The auto body repair industry operates within a framework of policies and regulations that vary by region, ensuring safety standards, consumer protection, and environmental compliance.
Vehicle Safety Standards: All vehicles must meet specific safety regulations, including structural integrity requirements for the body and frame. Repairs must adhere to these standards to ensure driver and passenger safety.
Environmental Protection: Regulations mandate proper disposal of automotive waste, such as solvents and scrap metal, and promote the use of eco-friendly materials and practices.
Consumer Protection: Laws protect consumers from fraudulent repairs, ensuring transparent pricing, quality work, and secure handling of personal vehicles during the repair process.
IHS Markit (Global Standards): IHS Markit provides global standards for vehicle design, testing, and repair procedures, serving as a reference point for many countries’ regulatory bodies.
International Organization for Standardization (ISO): ISO develops and publishes international standards, including those related to environmental management systems (e.g., ISO 14001) and quality management (ISO 9001), applicable to auto body repair facilities.
Regional Collaborations: Organizations like the European Union’s New Car Assessment Program (Euro NCAP) set safety standards for vehicles sold within the region, influencing auto body repair practices.
Despite its critical role, the auto body repair industry faces several challenges that impact its growth and reputation.
Skilled Labor Shortage: The highly skilled nature of auto body repair work poses a challenge in attracting and retaining qualified technicians, leading to potential backlogs and delayed repairs.
Technological Complexity: Keeping up with rapidly evolving technologies can be costly for shops, requiring significant investments in training, equipment, and software.
Competition from DIY Repairs: With the rise of online tutorials and do-it-yourself (DIY) resources, some minor repairs may be performed by vehicle owners themselves, potentially reducing the demand for professional services.
Environmental Concerns: The industry’s historical reliance on toxic materials and solvents has raised environmental awareness, pushing shops to adopt more eco-friendly practices.
Training Programs: Collaborating with vocational educational institutions and automotive manufacturers to develop comprehensive training programs can address the skilled labor shortage.
Government Incentives: Providing tax incentives or grants for shops that invest in advanced technologies can encourage digital transformation.
Marketing and Education: Industry associations can play a vital role in educating consumers about the benefits of professional repairs, countering the DIY trend.
Sustainable Practices: Promoting eco-friendly alternatives to traditional solvents and materials can help auto body repair shops meet environmental standards while appealing to environmentally conscious customers.
Japan is renowned for its meticulous approach to auto body repair, with highly skilled technicians known for their delicate handiwork. A leading Japanese repair shop, Tokyo Auto Art, exemplifies this tradition. They specialize in restoring classic and vintage vehicles to their original condition, employing traditional techniques alongside modern technology. Their attention to detail and commitment to preserving automotive history have earned them international acclaim. This case study highlights the fusion of heritage and innovation within the auto body repair process.
Germany’s auto industry is known for its precision engineering, and its auto body repair shops are no exception. A mid-sized German business, AutoReparatur Zentrum (ARZ), embraced digital transformation by implementing a comprehensive CAD/CAM system. This enabled them to streamline their operations, reduce labor costs, and offer faster turnaround times without compromising quality. ARZ’s success demonstrates the significant advantages of adopting advanced technologies in auto body repair.
In Brazil, a non-profit organization called “Reparo Comunitário” (Community Repair) has pioneered an innovative approach to auto body repair in low-income communities. They provide free or low-cost repairs to owners of essential vehicles, empowering local residents and promoting road safety. This case study highlights the social aspect of auto body repair, showcasing how industry professionals can contribute to community development.
The auto body repair process is poised for continued growth and transformation, driven by emerging technologies, evolving consumer preferences, and regulatory developments.
Autonomous Vehicle Repairs: As self-driving cars become more prevalent, a new set of repair challenges will arise, requiring specialized knowledge to address sensor damage and unique vehicle design features.
Advanced Materials: The use of composite materials, carbon fiber, and lightweight alloys in modern vehicles presents opportunities for repair shops to expand their service offerings and cater to manufacturers’ requirements.
Telematics and Remote Diagnostics: With telematics devices becoming standard in new cars, auto body repair shops can offer remote diagnostics, predictive maintenance, and real-time vehicle health monitoring services.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) Integration: AI-powered systems are expected to enhance quality control by analyzing repair data, identifying patterns, and suggesting optimal repair procedures.
3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing: 3D printing technology can revolutionize repairs by enabling the creation of custom parts, reducing waste, and offering cost savings in complex cases.
Virtual Reality (VR) Training: VR training simulations will provide immersive learning experiences for technicians, allowing them to practice complex procedures in a risk-free environment.
Digital Integration: Auto body repair shops should embrace digital transformation, implementing CAD/CAM systems, online booking platforms, and customer relationship management (CRM) software to enhance efficiency and customer engagement.
Sustainability Focus: Adopting eco-friendly practices not only addresses regulatory requirements but also appeals to environmentally conscious consumers, fostering long-term brand loyalty.
Adaptability: Staying agile in a rapidly changing industry is crucial. Shops should be prepared to adapt their business models and service offerings to accommodate new technologies and consumer trends.
The auto body repair process is more than just fixing damaged vehicles; it is an art, a science, and a vital component of modern mobility. As the automotive industry continues to evolve, so too will the demands placed on this critical sector. From embracing digital technology to addressing environmental concerns, auto body repair professionals are at the forefront of innovation, ensuring that vehicles not only run but also look their best for years to come.
As we look ahead, the future of auto body repair promises exciting possibilities, from advanced materials and autonomous vehicle repairs to AI-driven quality control and 3D printing innovations. By staying informed, investing in training, and adopting sustainable practices, industry players can navigate these trends successfully, ensuring a bright and resilient future for this essential service.
A: If your vehicle has significant dents, scratches, or damage to the body or frame, it’s best to consult a professional. They can assess the extent of the damage and provide recommendations for the best course of action. Minor dings and chips may be suitable for DIY repairs or touch-ups using PDR techniques.
A: Poor quality repairs may include uneven paint finishes, misaligned panels, excessive rust or corrosion, weak structural integrity, or visible gaps between repaired areas and surrounding surfaces. It’s essential to choose a reputable shop with skilled technicians to ensure high-quality work.
A: Start by asking for recommendations from friends and family who have had positive experiences. Check online reviews on platforms like Yelp or Google Maps. Visit local shops, inquire about their experience and training, and ask to see before-and-after examples of their work. Verifying certifications and ensuring they are insured is also crucial.
A: Absolutely! The auto body repair industry has historically contributed to environmental issues through the use of toxic solvents and hazardous waste generation. Reputable shops now prioritize eco-friendly practices, using water-based paints, solvent recovery systems, and recycling materials whenever possible to minimize their ecological footprint.
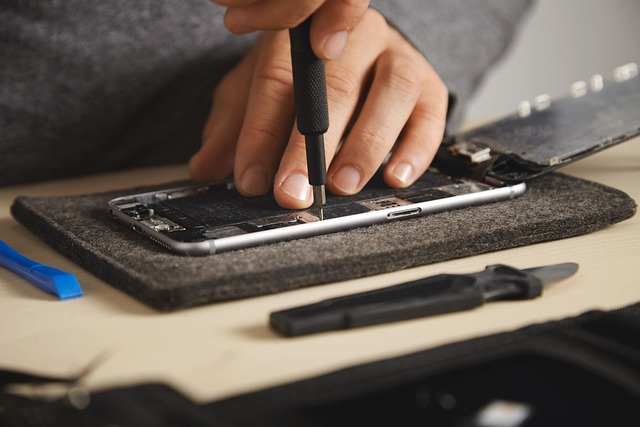

Collision and frame damage assessment is a critical first step in the auto body repair process, usin…….
Understanding the auto body repair process is key for vehicle owners facing damage. It begins with a…….

The auto body repair process, ranging from quick fixes to extensive restructuring after severe accid…….

In the meticulous world of auto body repair, every step from initial assessment to final refinishing…….
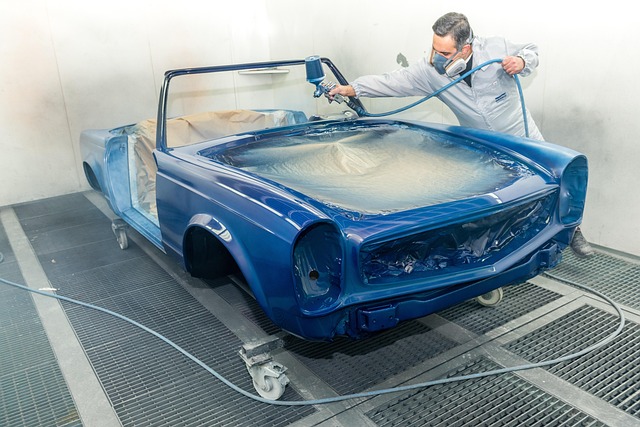

Safety inspections are paramount in auto body repair, prioritizing worker safety and vehicle integri…….

The first step in auto body repair is a comprehensive damage assessment conducted by skilled technic…….

After any collision, the auto body repair process begins with a comprehensive damage assessment. Ski…….

TL;DR: The initial step in auto body repair is a thorough damage assessment by skilled technicians,…….

Assessing damage is a critical step in auto body repair, involving meticulous inspection and diagnos…….

The auto body repair process involves assessing damage, using precise techniques like welding, patch…….